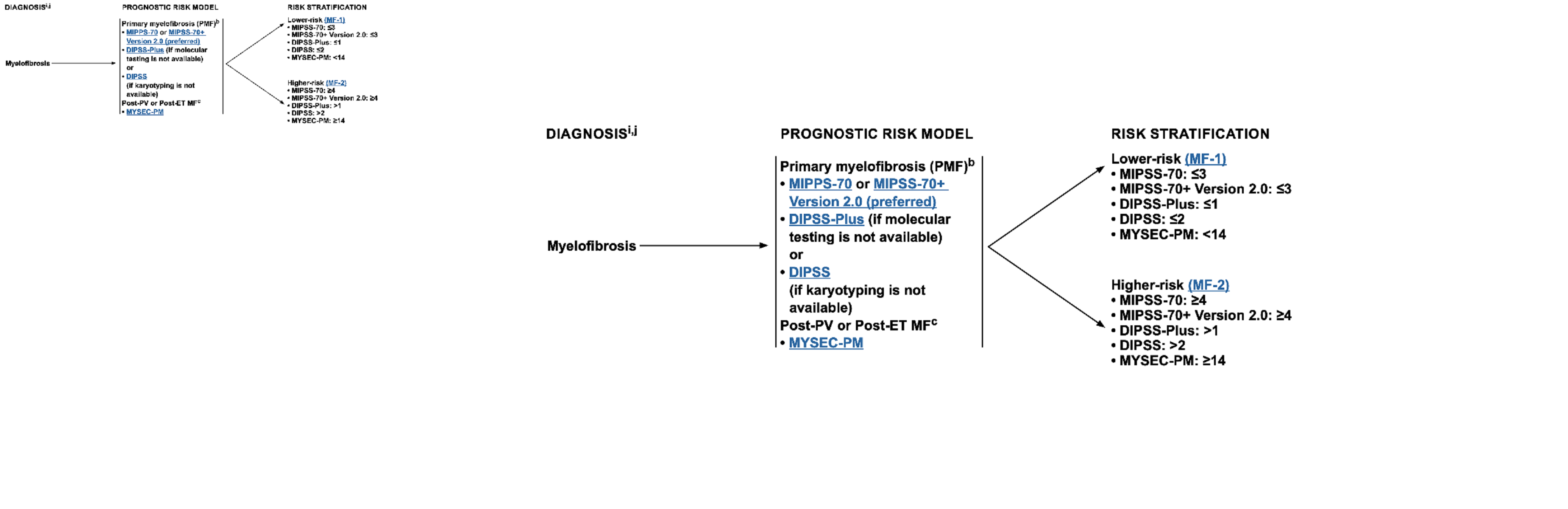
CBC normal values for Adult male
BY DR.MEGAN RALF · JULY 21, 2015
{{poster.name}} mentioned you in the group “{{group.name}}”: “{{usermessage}}” Go to the discussion to reply or catch up on the conversation: {{{mentioned.url}}}
Normal CBC test values that considered safe for age and sex of adult man.
Limits are according to universal guidelines.
CBC is a short for of “Complete Blood Count” which is a routine medical checkup test, CBC test show estimated counts of blood cells, CBC blood test useful for early detection of blood diseases and cancers.
Unit Count
HB g/dl 13.5-17.5
RBC 10^6/ul 4.5-5.9
HCT % 40-52
MCV fl 76-96
MCH pg 26-32
MCHC g/dl 33-37
RETICS % of RBCs 0.2-2.0
PLT *10^3/ul 150-400
WBC *10^3/ul 4000-11000
Differential leucocytic count: Absolute values/ul Percentage %
BASO less than 110 0-1
EOSINO less than 600 1-6
NEUTR 2000-8000 40-70
STAFF 0-5
SEGM 40-70
LYMPH 1500-4000 20-45
MONO 80-880 2-8
What do my CBC test normal ranges mean?
CBC normal values for Adult Female
BY DR.MEGAN RALF · JULY 24, 2015
{{poster.name}} replied to one of your comments: “{{usermessage}}” Go to the discussion to reply or catch up on the conversa tion: {{{thread.url}}}
What are the normal and healthy values for a mature female without a pregnancy?
The reference ranges chart define the healthy limits of complete blood cells count for women.
Values in this chart are considered safe for a women only if she’s no pregnancy episode.
Estimating the normal limits of women blood cells help in predicting early blood related diseases and cancers as well as bacterial or viral infections and follow up treatment effectiveness.
Unit Count
HB g/dl 12.0-16.0
RBC 10^6/ul 4.0-5.2
HCT % 37-47
MCV fl 76-96
MCH pg 27-32
MCHC g/dl 33-37
RETICS % of RBCs 0.2-2.0
PLT *10^3/ul 150-400
WBC *10^3/ul 4000-11000
Differential leucocytic count: Absolute values/ul Percentage %
BASO less than 110 0-1
EOSINO less than 500 1-6
NEUTR 1800-7500 40-70
STAFF 0-5
SEGM 40-70
LYMPH 1000-3500 20-45
MONO 80-880 2-8
What is the healthy normal ranges for a woman CBC test?
litelearning.com/resource-center/laboratory/interpreting-the-complete-blood-count-and-differential/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/4053-complete-blood-count
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7127472/
Tefferi et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005 Jul; 80(7): 923–936.
Published online 2011 Oct 20. doi: 10.4065/80.7.923
Reference Ranges of Complete Blood Cell Count in Adult White Persons and Persons of African Ancestry*
White
African
Variable Male Female Male Female
Hemoglobin9 (g/dL) 12.7-17.0 (13.5-17.5) 11.6-15.6 (12.0-15.5) 11.3–16.4 10.5–14.7
RBCs9 (× 1012/L) 4.0-5.6 (4.3-5.7) 3.8-5.2 (3.9-5.0) 3.8–5.7 3.6–5.2
⦁ Mean corpuscular volume⦁ 9 (fL) 81.2-101.4 (81.2-95.1) 81.1-99.8 (81.6-98.3) 77.4–103.7 74.2–100.9
RBC distribution width (%) (11.8-15.6) (11.9-15.5)
Platelets8 (× 109/L) 143-332 (150-450) 169-358 (150-450) 115–290 125–342
WBCs8 (× 109/L) 3.6-9.2 (3.5-10.5) 3.5-10.8 (3.5-10.5) 2.8–7.2 3.2–7.8
Neutrophils8 (× 109/L) 1.7-6.1 (1.7-7.0) 1.7-7.5 (1.7-7.0) 0.9–4.2 1.3–4.2
Lymphocytes8 (× 109/L) 1.0-2.9 (0.9-2.9) 0.95-3.3 (0.9-2.9) 1.0–3.2 1.1–3.6
Monocytes8 (× 109/L) 0.18-0.62 (0.3-0.9) 0.14-0.61 (0.3-0.9) 0.15–0.58 0.15–0.39
Eosinophils8 (× 109/L) 0.03-0.48 (0.05-0.50) 0.04-0.44 (0.05-0.50) 0.02–0.79 0.02–0.41
Basophils (× 109/L) (0-0.3) (0-0.3)
Open in a separate window
*Abstracted from population-based studies from Bain8 and NHANES-II. 9 Mayo Clinic normal values, based primarily on white subjects, are in parentheses for comparison. RBC = red blood cell; WBC = white blood cell.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/complete-blood-count/about/pac-20384919 Not a definitive test
A complete blood count is typically not a definitive diagnostic test. Depending on the reason your doctor recommended this test, results outside the normal range may or may not require follow-up. Your doctor may need to look at the results of a CBC along with results of other blood tests, or additional tests may be necessary.
For example, if you’re otherwise healthy and have no signs or symptoms of illness, results slightly outside the normal range on a complete blood count may not be a cause for concern, and follow-up may not be needed. Of if you’re undergoing cancer treatment, the results of a complete blood count outside the normal range may indicate a need
⦁
Not a definitive test
A complete blood count is typically not a definitive diagnostic test. Depending on the reason your doctor recommended this test, results outside the normal range may or may not require follow-up. Your doctor may need to look at the results of a CBC along with results of other blood tests, or additional tests may be necessary.
For example, if you’re otherwise healthy and have no signs or symptoms of illness, results slightly outside the normal range on a complete blood count may not be a cause for concern, and follow-up may not be needed. Of if you’re undergoing cancer treatment, the results of a complete blood count outside the normal range may indicate a need to alter your treatment plan.
In some cases, if your results are significantly above or below the normal ranges, your doctor may refer you to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist).
What the results may indicate
Results in the following areas above or below the normal ranges on a complete blood count may indicate a problem.
⦁ Red blood cell count, hemoglobin and hematocrit. The results of your red blood cell count, hemoglobin and hematocrit are related because they each measure aspects of your red blood cells.
If the measures in these three areas are lower than normal, you have anemia. Anemia causes fatigue and weakness. Anemia has many causes, including low levels of certain vitamins or iron, blood loss, or an underlying condition.
A red blood cell count that’s higher than normal (erythrocytosis), or high hemoglobin or hematocrit levels, could point to an underlying medical condition, such as polycythemia vera or heart disease.
⦁ White blood cell count. A low white blood cell count (leukopenia) may be caused by a medical condition, such as an autoimmune disorder that destroys white blood cells, bone marrow problems or cancer. Certain medications also can cause white blood cell counts to drop.
If your white blood cell count is higher than normal, you may have an infection or inflammation. Or, it could indicate that you have an immune system disorder or a bone marrow disease. A high white blood cell count can also be a reaction to medication.
⦁ Platelet count. A platelet count that’s lower than normal (thrombocytopenia) or higher than normal (thrombocytosis) is often a sign of an underlying medical condition, or it may be a side effect from medication. If your platelet count is outside the normal range, you’ll likely need additional tests to diagnose the cause.
For specifics about what your complete blood count results mean if they fall outside the normal ranges, talk to your doctor.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/complete-blood-count/about/pac-20384919
Normal CBC test values that considered safe for age and sex of adult man.
Limits are according to universal guidelines.
CBC is a short for of “Complete Blood Count” which is a routine medical checkup test, CBC test show estimated counts of blood cells, CBC blood test useful for early detection of blood diseases and cancers.
Unit Count
HB g/dl 13.5-17.5
RBC 10^6/ul 4.5-5.9
HCT % 40-52
MCV fl 76-96
MCH pg 26-32
MCHC g/dl 33-37
RETICS % of RBCs 0.2-2.0
PLT *10^3/ul 150-400
WBC *10^3/ul 4000-11000
Differential leucocytic count: Absolute values/ul Percentage %
BASO less than 110 0-1
EOSINO less than 600 1-6
NEUTR 2000-8000 40-70
STAFF 0-5
SEGM 40-70
LYMPH 1500-4000 20-45
MONO 80-880 2-8
What do my CBC test normal ranges mean?